What Is Bitcoin Mining and How Does It Work?
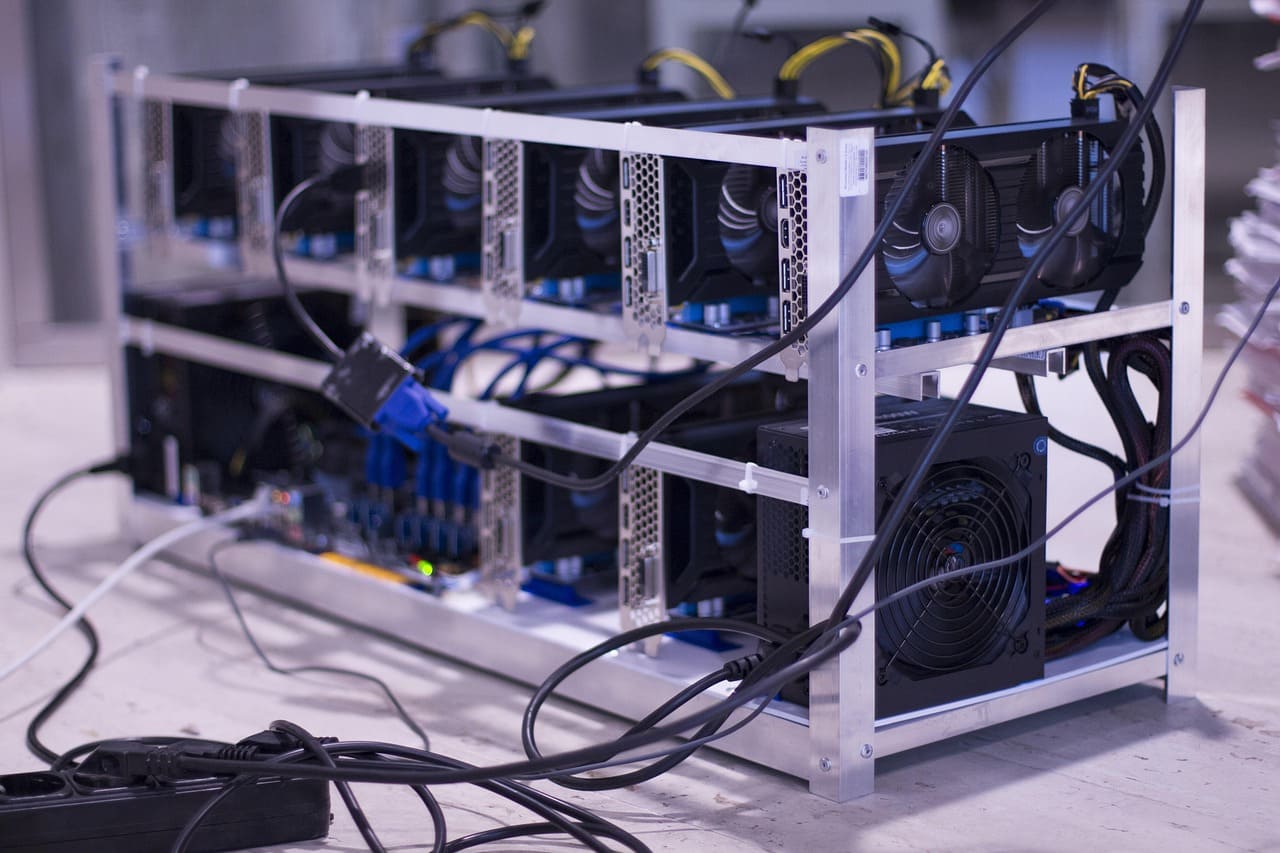

Bitcoin mining is the process by which new bitcoins are created and transactions are verified and added to the blockchain. It is a critical part of the Bitcoin network's decentralized system.
1. Why Is Mining Necessary?
Mining serves two main purposes:
- It creates new bitcoins through a process called block rewards.
- It secures the network by validating transactions and preventing double spending.
2. How Does Mining Work?
Miners use specialized hardware to solve complex mathematical puzzles. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets to add a new block to the blockchain and receives a reward in bitcoins.
3. The Role of Proof of Work
Bitcoin uses a consensus mechanism called Proof of Work (PoW). This requires miners to expend computational energy to solve puzzles, making the system secure and tamper-resistant.
4. Mining Rewards
When a miner successfully adds a block, they earn:
- Block reward: A fixed number of new bitcoins (which halves approximately every four years).
- Transaction fees: Collected from users who send transactions.
5. Mining Difficulty
The Bitcoin network adjusts the difficulty of puzzles every 2,016 blocks (~2 weeks) to ensure a steady block production rate of about one every 10 minutes.
6. Conclusion
Bitcoin mining is fundamental to the operation and security of the Bitcoin network. Though competitive and energy-intensive, it ensures that the system remains decentralized and reliable.